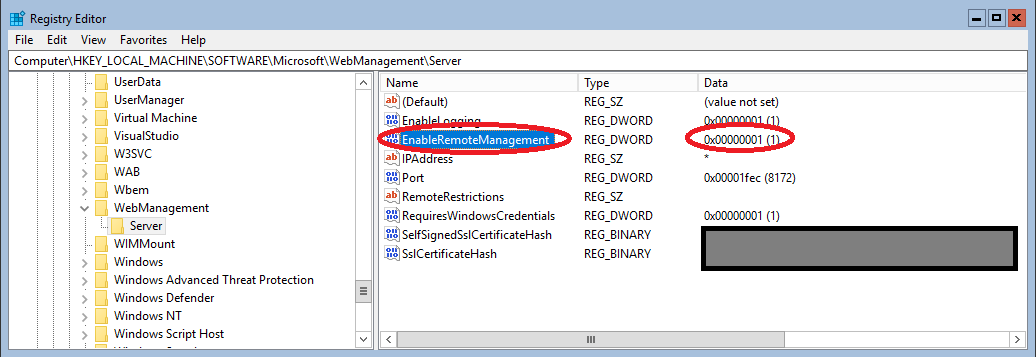
There may be a situation where you wish to completely reinstall WSUS from scratch. This can occur for a number of reasons, but most commonly is due to database corruption, or performance issues due to a WSUS database that hasn’t been maintained properly with the normal maintenance.
Commonly, when regular maintenance hasn’t occurred on a WSUS database, when an admin finally performs it, it can take days and weeks to re-index the database, clean up the database, and run the cleanup wizards.
Also, due to timeouts on IIS, the cleanup wizard may fail which could ultimately cause database corruption.
Administrators often want or choose to blast away their WSUS install, and completely start from scratch. I’ve done this numerous times in my own environment as well as numerous customer environments.
In this guide, we are going to assume that you’re running WSUS on a Windows Server that is dedicated to WSUS and is using the WID (Windows Internal Database) which is essentially a built-in version of SQL Express.
PLEASE NOTE: If you are using Microsoft SQL, these instructions will not apply to you and will require modification. Only use these instructions if the above applies to you.
What’s involved
WSUS (Windows Server Update Services) relies on numerous Windows roles and features to function. As part of the instructions we’ll need to completely clear out:
- WSUS Role, Configuration, and Folders/Files
- IIS Role, Configuration, and Folders/Files
- WID Feature, Configuration, and Database Files
Since we are completely removing IIS (Role, Configuration, and Folders/Files), only proceed if the server is dedicated to WSUS. If you are using IIS for anything else, this will completely clear the configuration and files. You also do not want to run this on a domain controller as Active Directory also uses WID.
Let’s get to it!
Instructions
- Open “Server Manager” either on the host, or remotely and connect to the host you’d like to reinstall on.
- Open “Remove Roles and Features” wizard.
- Click “Next”, and select the Server, and click “Next” again.
- On the “Remove server roles” screen, under “Roles”, we want to de-select the following: “Web Server (IIS)” and “Windows Server Update Services” as shown below.
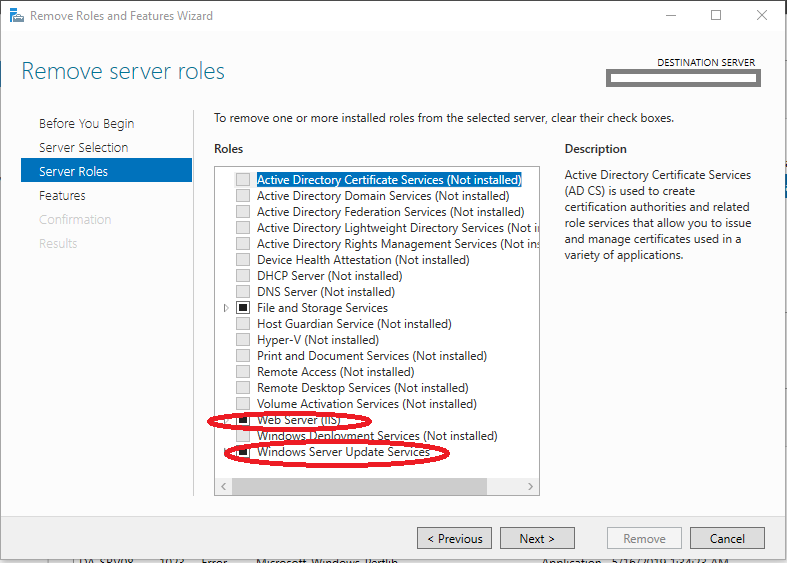
- Click “Next”
- On the “Remove features” screen, under “Features”, we want to de-select the following: “Windows Internal Database” and “Windows Process Activation Service” as shown below.
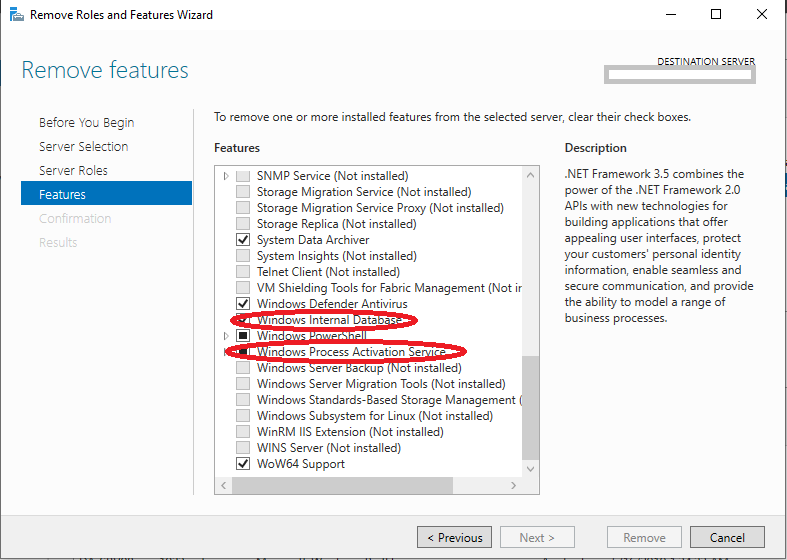
- Click “Next” and follow the wizard to completion and remove the roles and features.
- Restart the Server.
- Open an administrative command prompt on the server, and run the command “powershell” or open powershell directly.
- Run the following command in powershell to remove any bits and pieces:
Remove-WindowsFeature -Name UpdateServices,UpdateServices-DB,UpdateServices-RSAT,UpdateServices-API
- Restart the Server.
- We now must delete the WSUS folders and files. Delete the following folders:
C:\WSUS C:\Program Files\Update Services
Note: You may have stored the WSUS content directory somewhere else, please delete this as well. - We now must delete the IIS folders and files (and configuration, including the WsusPool application pool, bindings, etc.). Delete the following folders:
C:\inetpub C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv
Note: You may have issues deleting the “inetsrv” directory. If this occurs, simply rename it to “inetsrv.bad”. - We now must delete the WID (Windows Internal Database) folders and files (including the WSUS SQL Express database). Delete the following folder:
C:\Windows\WID
- While we removed the IIS folders and files, we deleted a needed system file. Run the following command to restore the file:
sfc /scannow
- Restart the Server.
WSUS, IIS, and WID have at this point been completely removed. We will now proceed to install, apply a memory fix, and configure WSUS.
For instructions on installing WSUS on Server Core, please click here: https://www.stephenwagner.com/2019/05/15/guide-using-installing-wsus-windows-server-core-2019/
- Open “powershell” (by typing powershell) and Install the WSUS Role with the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature UpdateServices -Restart
- (Optional) If you want to install the WSUS MMC Snap-In/GUI, run the following command in the powershell window:
Install-WindowsFeature UpdateServices-RSAT, UpdateServices-UI
- Run the post installation task command in command prompt to configure WSUS:
"C:\Program Files\Update Services\Tools\wsusutil.exe" postinstall CONTENT_DIR=C:\WSUS
- AT THIS POINT DO NOT CONTINUE CONFIGURING WSUS AS YOU MUST APPLY A MEMORY FIX TO IIS.
- Apply the “Private Memory Limit (KB)” fix as provided here: https://www.stephenwagner.com/2019/05/14/wsus-iis-memory-issue-error-connection-error/
- Restart the Server.
- Open the WSUS MMC on the server or remotely from a workstation on the network and connect it to the WSUS instance on your Server Core install.
- Run through the wizard as you would normally and perform an synchronization.
- WSUS has been re-installed.
And that’s it. You’ve completely reinstalled WSUS from scratch on your Windows Server.